-
Behaviour Scoring
-
- 1. Anxious in unfamiliar situations
- 2. Fear Of Noises
- 3. Fear of Novel Objects
- 4. Fear of Underfootings
- 5. Fear of Dogs
- 6. Fear of Stairs
- 7. Fear of Traffic
- 8. Separation Anxiety
- 9. Hyper-Attachment
- 10. Fear Of Strangers
- 11. Body Handling Concern
- 12. Retreats When Reached For
- 13. Harness Handle On Back Sensitivity
- 14. Avoidance Of Blowing Fan
- 15. Body Sensitivity To Object Contact
- 16. Anxious About Riding In Vehicles
- 17. Inhibited or passively avoidant when exposed to potentially stressful situations
- 18. Activated when exposed to potentially stressful situations
- 19. Excitable
- 20. Slow To Return To Productive Emotional State
- 21. Fidgety When Handler Is Idle
- 22. Fear On Elevated Areas, Drop-Offs Etc.
- 23. Barks Persistently
- 24. High Energy Level
- 25. Lacks Focus
- 26. Movement Excites
- 27. Chasing Animals
- 28. Dog Distraction
- 29. Sniffing
- 30. Scavenges
- 31. Inappropriate Behavior Around The Home
- 32. Lacks Initiative
- 33. Not Willing
- 34. Resource Guarding Toward People
- 35. Aggression Toward Strangers
- 36. Aggression Toward Dogs
- 37. Resource Guarding Toward Dogs Or Other Pets
- 38. Inappropriate Elimination While Working En Route
- 39. Socially Inappropriate Behavior With People
- 40. Inconsistent
- 41. Handler/Dog Team
- 42. Relationship Skills
- 43. Comparison 9 To 1 Score
- 44. Socially Inappropriate Behavior With Dogs
- 45. Thunder Reaction Prior To, During Or Immediately After A Thunderstorm
- 46. Kennels Poorly
- 47. Working Speed
- 48. Gait When Moving Out
- 49. Housebreaking Problems
- 50. Innate Desire To Work
- 51. Avoidance Of Exhaust From Vehicles
- Show all articles ( 36 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Practice Videos
-
Behavior Testing
-
Database User Manual
-
-
-
- Adding a New Dog (using Manage Your Dog’s Data, MyDogs)
- Alerts
- BCL, Behavior Checklist
- Elbow Quick, Add new
- Estrus & Whelps
- Eye Quick
- Genetic Test Panel
- Genetic Test Quick
- Health Diagnoses Add/Edit
- Health History Report
- Health Normals, Add new
- Heart Quick
- Hip BVA, Add new
- Hip FCI, Add new
- Hip OFA, Add new
- Hip Penn Hip, Add new
- Photos PDFs etc.
- Private Notes
- Procedures, Add new
- Reminders
- Share my dog data to another organization
- Skin Quick
- Status History
- Weight - Entering a dog's weight
- ADI Public Access Test
- Hip Vezzoni, Add new
- Status Detail
- Edit or Change Call Name / Pedigree Name / Owner ID
- Add New Microchip / Delete Incorrect Microchip
- End Reasons
- Juvenile Estrus
- Communications Activities
- Incidents
- Show all articles ( 18 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
- Alternate Therapy/Rehab
- Diagnostic Imaging, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Diet
- Elbow Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Estrus & Whelps, Add new
- Eye Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Genetic Test Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Health Diagnoses, Add new / Edit (Update) or Delete
- Health History Report, Generate a PDF
- Health Normals
- Health Screening List
- Hip OFA Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hip Penn Hip Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hospitalization, Add new
- Kennel Tasks, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Lab, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Photos, PDFs, etc., Add new
- Reminders Add new / Edit or Delete
- Rx, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Semen Cryo, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Skin Quick Add new / Edit or Delete
- SOAP, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Status History
- Supplies Used, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Surgery, Add new
- Treatments Add new / Edit or Delete
- Vaccines Add new / Edit or Delete
- Weight and BCS Body Condition Score - Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hip Vezzoni, Add new
- Show all articles ( 14 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
Early Socialization
-
- Video - Coat Desensitization
- Video - Novel Objects
- Video - Trolley Ride with Mom
- Early Puppy Socialization - Novel Objects video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Novel Sounds video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Introducing New Environments video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Motor Development, Balance, Coordination, Proprioception video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Passive Environmental Enrichment in the Den video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Stairs
-
-
Genetic Selection & Inbreeding
-
- What are EBVs and how do they help?
- How EBVs are calculated
- What is needed to calculate EBVs and EBV accuracy?
- Using EBVs effectively
- Selection index
- Why are EBVs different for littermates?
- Presentation Recording: Improving behavior using EBVs
- Presentation Recording: Using EBVs successfully
- Presentation Recording - Improving health using EBVs
-
Webinars
-
Reproduction
-
Organization Management
Types of Mating
Natural Matings have the highest success for conception of all techniques available. Using an inexperienced stud for natural matings often requires “Sex Education” using a calm, experienced bitch in prime estrus, ideally the bitch he is to mate. The education sessions should be quick, lasting no more than 5 minutes, and supervised 3-5 times daily to encourage mating behaviors such as mounting, thrusting, and (if possible) allowing mating. While supervising, provide positive reinforcement only. Generally, one successful mating is all the training a stud needs to become proficient at the task.
Each stud is different. Some prefer no human intervention, while others do well with a handler applying upward pressure on the stud’s pelvis below the tail to ensure that the bulbus glandis is inside the bitch prior to engorgement. Contractions from the vaginal muscles of the bitch maintain pressure behind the bulbus glandis, which is what maintains the erection. When the bitch’s muscles relax, pressure is reduced, allowing the erection to end.
Outside ties occur when the bulbus glandis is able to engorge outside of the vagina of the brood, thus preventing a “tie”; the penis is able to slip out of the vagina. If an outside tie occurs, elevate the bitch’s hind end and feather the vagina when this occurs. Repeat the mating in several hours in hopes of complete tie.
Studs that routinely have outside ties need to be evaluated for the following:
- Pain – joint or spinal pain in the stud
- Lack of libido
- Psychological – some young guide dogs studs have been so well-raised to not jump on people or furniture, that they are unsure of mounting the bitch.
- Bulbus glandis diameter- the engorged bulbus glandis is too small in diameter (5 cm versus 5.6 cm in Labrador Retrievers) for the bitch’s vaginal tract even when she is contracting her vaginal muscles. In this instance, vaginal or transcervical inseminations with fresh semen are necessary. Studies at Guiding Eyes for the Blind on bulbus glandis diameter indicated sons from a stud with a small bulbus glandis (50 mm) had normal diameter bulbus glandis.
Chilled and Frozen Semen
Chilled Semen is an ideal way of using studs that are beyond driving distance. The sperm-rich fraction only is collected into extender such as Fresh Express™, which is available from vendors such as Synbiotics. After processing by slow cooling, it is shipped on ice to the bitch. Insemination can be done vaginally or transcervically.
Frozen Semen is the preferred method of utilizing semen from dogs from other countries or at later time periods when the stud dog is no longer available. Insemination can be done surgically, transcervically or, with some protocols, vaginally. The results with transcervical insemination can be as high as 80% conception and average litter sizes of 6 puppies.
Transcervical Insemination (TCI)
This insemination procedure was developed by Dr. Marion Wilson, BVMS, MVCS, MRCVS around 1992. A vaginoscope is inserted into the vagina with the aid of a fiber-optic telescope in the shaft of the vaginoscope. When the cervix is located in the anterior vagina, a catheter that is also in the shaft of the vaginoscope is used to manipulate the opening to the cervix (cervical os) and the catheter is passed into the uterus. The semen (which can be fresh, chilled or frozen) is gently injected through the catheter into the uterus. This procedure provides a very viable alternative to surgical insemination with no untoward side effects for the bitch.
When using frozen semen, sperm only lives about 12-24 hours after thawed, and it has poor ability to transverse the cervix. Intrauterine insemination increases the chance of conception.
Conception rates are as follows:
- Vaginal – 30%,
- Intrauterine- 50% to 80%
There are 2 intrauterine methods:
- Surgical- 1x, anesthesia
- Transcervical- multiple times
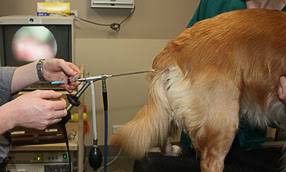
Trans Cervical Insemination video:
The equipment required for this procedure and the equipment needed to store and handle frozen semen totals about $19,000 US Dollars as of 5/2006. It does require staff training, which can be taught in about three days. Guiding Eyes for the Blind (guidingeyes.org) has provided training to multiple schools around the world and can be contacted if training or more information is desired.
Semen Quality and Success With AI
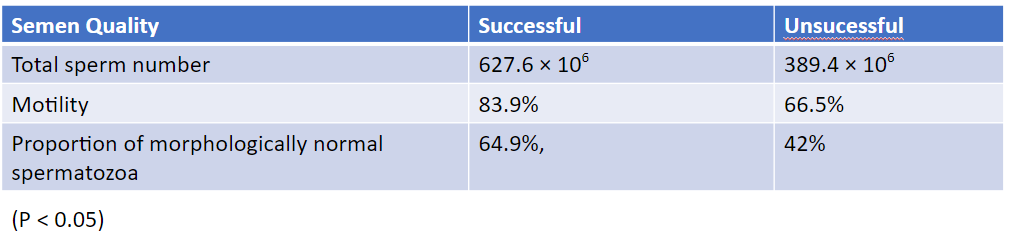
Variables affecting semen quality and its relation to fertility in the dog: A retrospective study.
Tesi M1, Sabatini C2, Vannozzi I2, Di Petta G2, Panzani D2, Camillo F2, Rota A2. Italy https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29883842
